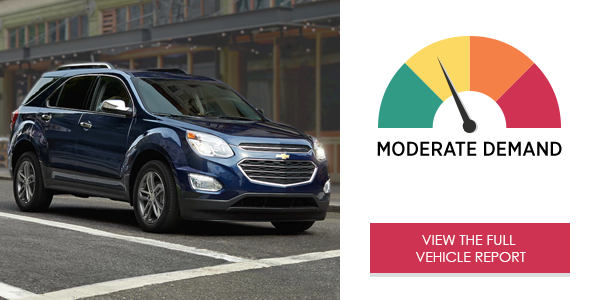
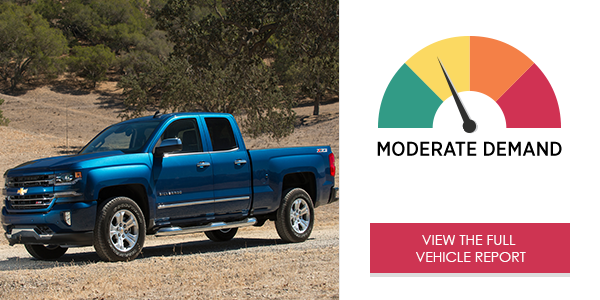
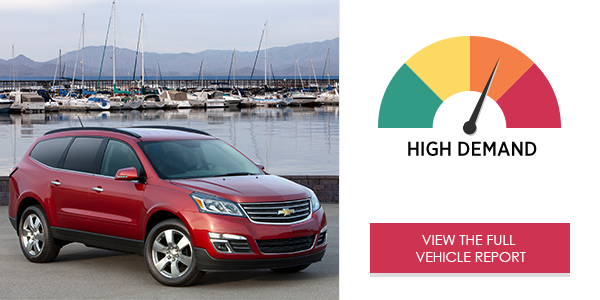
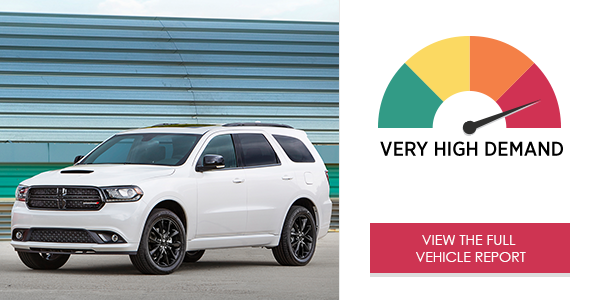
AAA’s Center for Driving Safety & Technology, working with the researchers at the University of Utah, examined the visual (eyes-off-road) and cognitive (mental) demand as well as the time it took drivers to complete a task using the infotainment systems in 40 2017 and 2018 vehicles*. Study participants were required to use voice command, touch screen and other interactive technologies to make a call, send a text message, program audio entertainment or program navigation, all while driving down the road. None of the 40 vehicle infotainment systems produced low demand, while 29 systems generated high or very high levels of demand on drivers.
Vehicle reports are available for each vehicle’s information system that was evaluated. Consumers can use these results to learn more about the system found in their current vehicle and/or to inform their next vehicle purchase. Automakers and other industry players can leverage these results to isolate the most significant sources of driver demand generated by use of their products, and to enhance these designs such that they minimize the demands placed on people who use them while driving.
The 2018 BMW 430i xDrive infotainment system* placed very high demand on drivers in the study. While the voice system interpreted commands for audio entertainment and phone functions easily and quickly, the center stack rotary wheel imposed very high demand levels on drivers when used for navigation.
The 2017 Buick Enclave Leather’s IntelliLink infotainment system* placed very high demand on drivers in the study. Center stack functions required very high demand due to the small buttons and the nonintuitive design of the system. Using the voice command structure to send text messages proved particularly demanding.
The Cadillac XT5 Luxury Cadillac User Experience (CUE) infotainment system generated high demand on drivers when placing phone calls and programming the navigation system. The Cadillac XT5’s voice system was accurate and simple to use. However, the touch screen generates very high cogntive (mental) and visual (eyes-off-road) demand.
The 2017 Dodge Durango GT with Uconnect® 8.4 NAV infotainment imposed very high demand on drivers in the on-road study when used for phone calls, text messaging, audio entertainment and navigation. While drivers were able to quickly place calls and make audio selections, doing so required very high visual (eyes-off-road) demand.
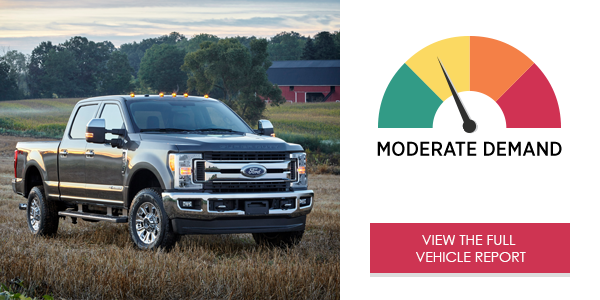
The Dodge Ram 1500 Express’ Uconnect® infotainment system placed high demand levels on drivers using it for phone calls, audio entertainment and text messaging. While interactions with the infotainment system in the Dodge Ram were typically short, drivers experienced high cognitive and visual demand. The system could benefit from a larger screen and a more natural sounding voice.
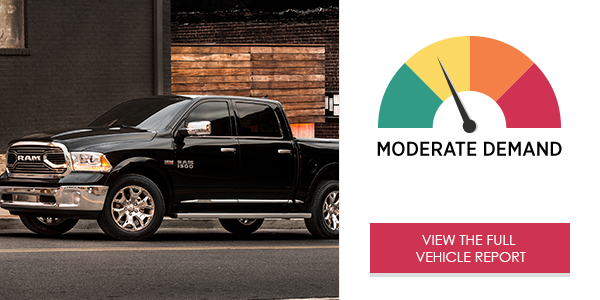
The 2018 Ram 1500 Laramie’s Uconnect® infotainment system* placed moderate demand on drivers in the study. Drivers can use either the voice system or center stack to quickly program audio entertainment or place calls. In contrast, sending text messages via voice generated very high levels of demand overall.
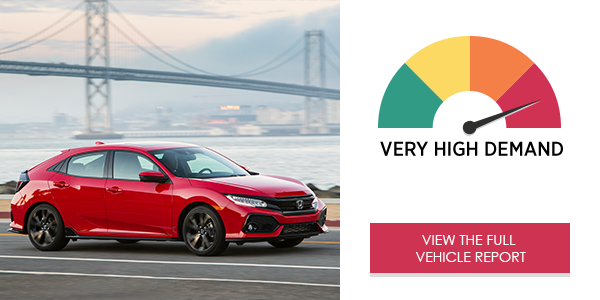
The 2017 Honda Civic Sedan Touring’s HondaLink® infotainment system placed very high demand on drivers using it for phone calls, text messaging, audio entertainment and navigation. The system would benefit from faster processing time, both for voice commands and touch-screen interactions, and a navigation system design that is consistent with the design of the rest of the system.
The Honda Ridgeline RTL-E’s HondaLink® infotainment system (version 4.2.2) generated very high demand in the study, requiring an excessive amount of time to place calls, send text messages, program navigation and adjust audio. Most notably, the audio and turn-by-turn navigation system are very highly demanding and time-consuming.
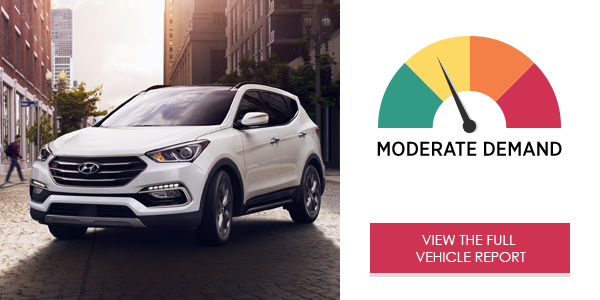
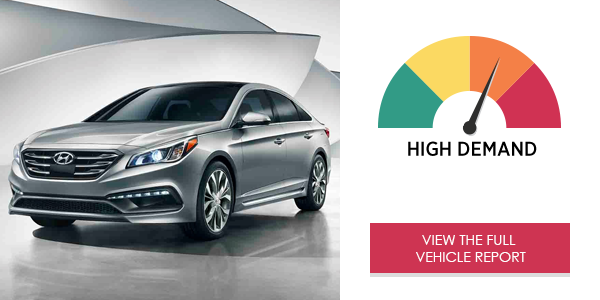
The Hyundai Sonata Base’s Blue Link® infotainment system placed high demand on drivers. The voice system is quick and intuitive but could be improved with a simpler process for dialing phone numbers. The center stack touch-screen menu offers quick access to core functions and the information is presented in a neat but cramped format.
The 2017 Infiniti Q50 Premium AWD’s InTouch® infotainment system generated an overall moderate demand in the study. Drivers who placed calls and adjusted audio using voice commands or the center stack and console experienced moderate demand. However, using the text messaging system posed very high overall demand.
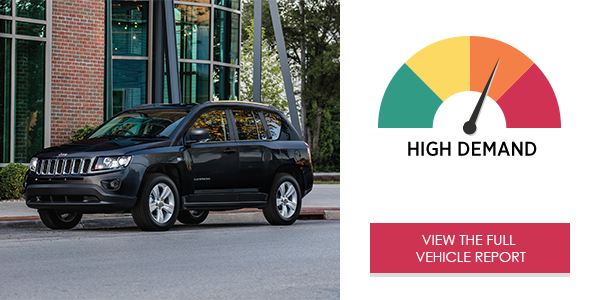
The Jeep Compass Sport’s Uconnect® Radio 230/REQ infotainment system received an overall high demand rating. Text messaging and audio entertainment processes required very high degrees of cognitive (mental) demand to complete tasks. The Jeep Compass’ interface allowed drivers to complete most interactions, other than text messaging, quickly.
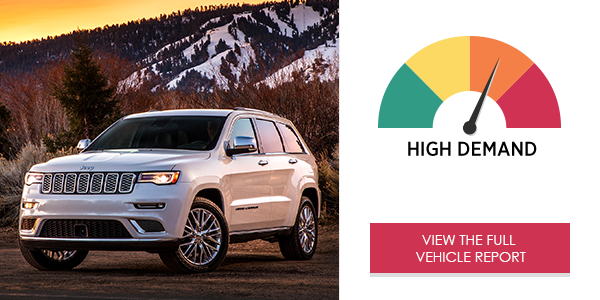
The Jeep Grand Cherokee Limited’s Uconnect® infotainment system received an overall high demand rating. Using either voice commands or the touch screen, calling and dialing tasks are quick and generate an overall moderate demand on drivers. However, many texting tasks place high overall demand on drivers, and using navigation requires even higher demand.
<p><a href=”/wp-content/uploads/2018/06/18-0303_AAAFTS_CDST-Vehicle-Report_Kia-Optima_FINAL.pdf” target=”_blank” rel=”noopener”><img class=”alignnone wp-image-8378 size-full aligncenter” src=”/wp-content/uploads/2018/06/Kia-Optima.png” alt=”” width=”600″ height=”300″ /></a></p>
<p>The 2018 Kia Optima LX UVO® infotainment system* placed moderate demand on drivers in the study. The voice command system allowed users to easily place calls and program audio entertainment, although using the center stack placed very high levels of visual (eyes-off-road) demand on drivers.</p>
The 2017 Land Rover Range Rover Sport HSE InControl® infotainment system* placed very high overall demand on drivers in the study. Voice commands for audio entertainment and phone calling were kept short although at the cost of higher cognitive (mental) demand. Of note, using the touch screen to access the navigation system and audio entertainment imposed very high overall demand.
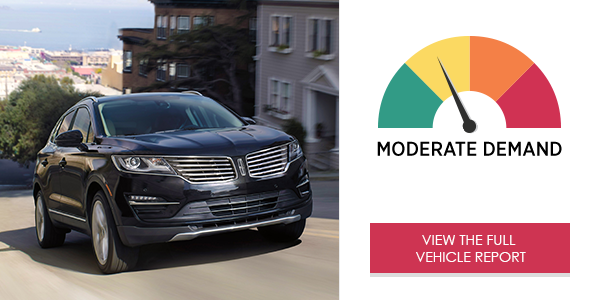
The 2018 Lincoln Navigator Select L SYNC 3 infotainment system placed overall moderate demand on drivers in the study. Use of the system generated high visual (eyes-off-road) demand. Short, simple commands and a easy to use touch screen design allowed for short interactions to change the radio, send text messages and place phone calls. However, navigation tasks required lengthier interactions.
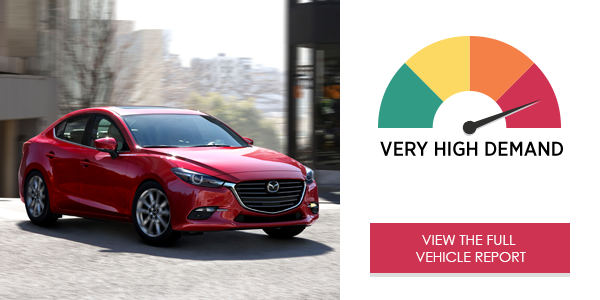
The 2017 Mazda3 Touring’s Mazda Connect™ infotainment system imposed very high demand on drivers in the on-road study. Drivers were not able to efficiently use the center console to place phone calls and make audio changes, most likely due to the system’s complex menu structure. Accessing the text messaging menu using voice commands or the center stack proved to be a highly demanding task.
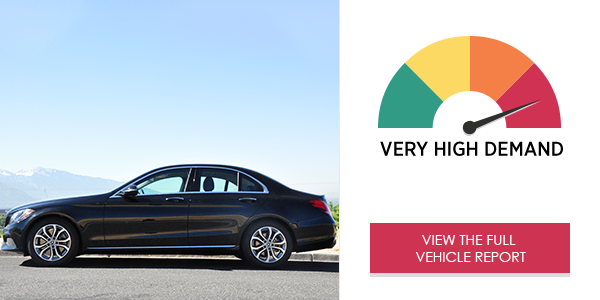
The Mercedes-Benz C300’s COMAND® infotainment system* received an overall very high demand rating in the study. Drivers’ visual (eyes-off-road) and cognitive (mental) attention was drawn away from the road as they attempted to navigate the center stack menu using a rotary control. This produced overall very high levels of demand for all functionalities.
The 2017 Nissan Armada SV NissanConnect® infotainment system imposed a very high demand on drivers in the on-road study. While the phone and audio entertainment facets of the system placed moderate demand on drivers, the cumbersome navigation system was so difficult to use that it negatively impacted the overall performance of the Armada. Drivers were unable to quickly search through the complex navigation menu on the center stack or use the system-specific voice commands to set destinations while remaining focused on the road.
The 2018 Nissan Pathfinder SL’s NissanConnect infotainment system placed very high demand on drivers in the study. While the system reacts quickly and allows drivers to promptly place calls and change the audio, the navigation and text messaging functions generated very high cognitive (mental) demand for extended periods of time.
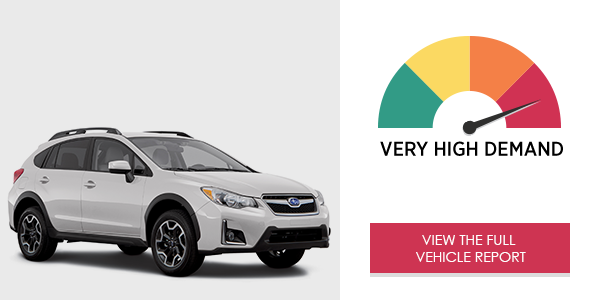
The Subaru Crosstrek with STARLINK™ infotainment system placed very high demand on drivers using it to place phone calls and adjust audio entertainment. In its current state, drivers may become frustrated by the system’s non-intuitive and time-consuming processes, especially when using voice commands.
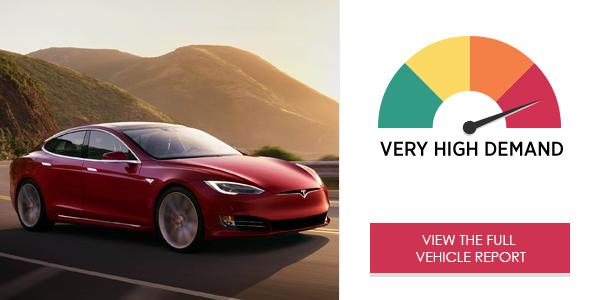
The Tesla Model S 75 infotainment system generated a very high demand rating in the study. The system was very highly demanding on drivers when placing phone calls, tuning the audio system and programming the navigation. Interacting with the infotainment system leads to very high distraction from the forward roadway.
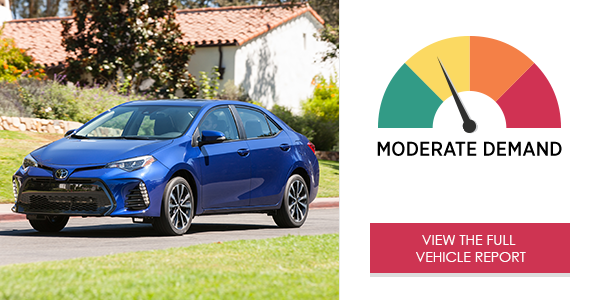
The Toyota Corolla SE with Entune™ generated overall high demand on drivers in the study. Accessing phone functions, sending text messages, and selecting audio entertainment via the center stack required little time, but imposed very high cognitive (mental) demand, while voice commands proved better.
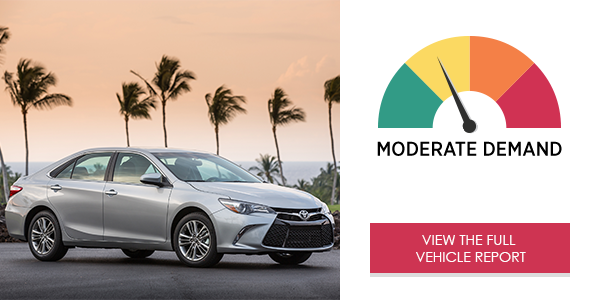
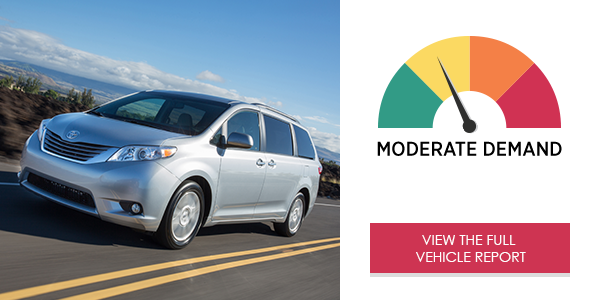
The 2017 Toyota Sienna XLE Entune™ infotainment system generated an overall moderate demand level. The limited options presented in the center stack phone and audio menus resulted in quick interactions, although very high cognitive (mental) demand levels were observed. Text messaging proved to be a highly demanding interaction, due in part to the text-heavy design of the messaging menu.
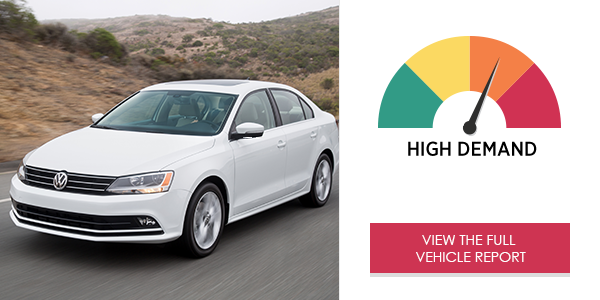
The 2017 Volkswagen Jetta S MIB II® infotainment system* placed high demand on drivers in the study. Infotainment functions are only accessible via the touch screen; voice command is not available in this vehicle. Making audio entertainment selections and placing phone calls produced very high visual (eyes-off-road) and cognitive (mental) demand.
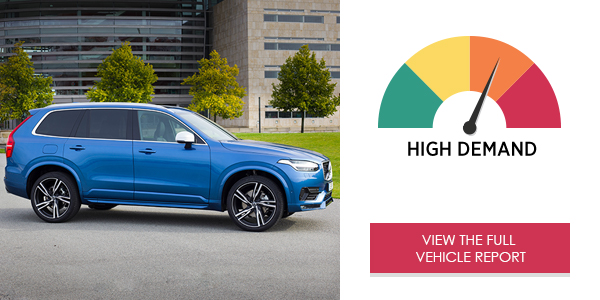
The Volvo XC60 T5 Inscription’s Sensus Connect infotainment system created very high demand levels in the on-road study for phone calls, text messaging , and navigation. Overall, the XC60 system had poor on-road performances, in terms of low usability and high levels of demand. Drivers were free to operate the vast majority of the system, unchecked, while the vehicle was in motion.